What’s “SMART GRID”
If you separate the word in two pieces, you can see it as “smart” and “grid”. As IT technology evolves, not only smart-phone but also grid itself is starting to make an evolution from analog era.
So what is that evolution? Simply put, it is to make it possible to transmit the electricity efficiently after knowing the demand of energy in real-time. In the case of America, they started investigating this technology 10 years ago and gathered the attention again under the Obama administration to start making it more practical. Occasionally it is translated as “the next generation of power line/ the next generation of energy system.
Then how come it is called smart? From the electric meter attached to our house, we can not tell the electricity being consumed in real-time. So, the introduction of the electric meter called “Smart Meter” with Internet network, can help us send the data to an electric company in real time or predict the consumption of the electricity in the future precisely.
Accordingly from an electric company’s point of view, it can respond to supply the demand in real time, or it can tell the consumer to save the power when it realizes it is not possible to supply the power enough. Therefore, we will be able to save a lot of loss after knowing the needs among supplies and demands interactively. This system also includes what we call a regenerated energy such as the wind power generation and solar power, and interactivity among those different power generation system to make it efficient is investigated also.
And this interactive energy system generated by the fusion between IT technology and energy will be extended to rebuild our city to consider the environment and resources for the next generation.
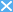
● Smart City > Energy management
・Visualization of the energy in the household using a system of HEMS
・Management of the energy in the building using a system of BEMS
・Management of energy in the city using a system of CEMS
Why Smart Grid? The reason for Japanese electric situation.
It is said that Japanese power network possess the stableness and efficiency at the top level of the world. “Smart Grid” itself used be only considered as one the ways to make the electric system more stable.
However, after 11th of March, Japanese electric situation has been changed drastically. It may be good time for us to face the nature, power and the society now. As we often see saying as “Supply and Demand of the power is tight” now, we temporarily look at the issue from three process, generate, transmit, and consume, we can grasp the issues as following:
1) Secure the resources for power generation. How we should deal with the nuclear power. The issue of the substituted energy, and how we should deal with the features that can not be stored.
2) The issue of a difference of a radio frequency between west and east Japan. “The issue of energy loss” meaning 60% of a total power transmitted is lost before the power reaches the demands.
3) How to use the electric such as how we should save the electric or target such an environment where the demands can consume the power in the most optimised way.
Smart grid can be one the ways to solve the above issues inter-disciplinary using the technology of the next generation. In the laboratory of Ida, especially we are focusing on above issues, and from an economic point of view we hold up a keyword of “Social Proof” to deal with the researching.
Smart Grid and economics?
We can not live with out economical activity. This “economy” has a vast meaning, not only for the money but also include the limited resources in the world. Generally speaking economics seem to be very difficult subjects using tough mathematics or analyzing very complex subject, but rather it is to achieve the “distribution of the resources in the most optimized way”. In order for us to improve our life standards, this academic field is the most near-by study to think about how and what to distribute in the most efficient way.
In regards of electricity, we need to consider how we should distribute it especially under such circumstances as we are in short of the supplying power.
After 11th March, even though we have become more aware of saving the electricity, how should we save the electricity concretely? What is the efficient way to save the electricity?
There is a word saying “Demand Response (DR)”. This is the system where the electric company tells demands to save the power in short of the power supply in order to make a change of the consumption pattern of the power.
And to make the demands change their behavior, there are big categories as below. By the way, making a change of the price of the electricity considering the supply/demand of the power, we call it Dynamic Pricing (Fluctuating style of the electric price).
System 1: Based on the price of the electricity
Example) We change the price of the electricity in the time zone, and we charge more at the peak of its demand.
System 2: Based on incentives
Example) Close or provide such a contract which brings the benefit to the extend people save the electric.
By the way, in the laboratory of Ida, there was a research of how quitting a Tabaco and its price affect each other. From this, we learned that Tabaco price and ratio of peoples’ determination of quitting as follows; 25% to 400 Yen, 41% to 500 Yen, 62% to 600 yen, 81% to 700 yen, 92 % to 800.
If you want to know this more, please see the below webpage.
And such as the case above, we think of how the price would affect the people’s behavior to save the electric. For instance, if we raise the price to 24 yen per 1 kw, how much do you think people can save the electricity?
Setting the highest temperature at 35℃ in the certain summer time, and when we raise the price from 35, 40, 50, and 60 yen to predict how the household respond to it, from those behavior patterns we calculated how much electricity had been saved at the peak of the summer time.
The result was we could have calculated as follows: 128kw was saved at 35yen, 139kw at 40 yen, 157kw at 50 yen, and 175kw at 60 yen.
We should not raise the price blindly. But for example, if we raise the electric price at the peak of its demand, and lower it at the off peak of demand, it may affect the demand at the peak. Because we can not save the electricity, we will have a huge power failure in a moment when demand exceeds the supply.
Since the 1/3 of demand at its peak is coming from households, we really need to come up with the concrete solution.
However, as described at the beginning, we can not know how it will work at this moment. So it is likely that if demands would take more actions toward saving electricity more if they see the price and the situation consciously using a smart meter. DR gains the attention and is expected to provide the efficient system that promotes demeand’s behavior of saving the electric and their cooperation also.
Also, at laboratory of Ida, we expect that DR system itself is not enough to change the whole situation. For instance, in order to introduce DR, not only pricing and its system should be studied but also mental and behavior attitude should be researched also. (For those who are interested in learning more about this, please see the overview of the project “Research on behavioral economics of demand and response of energy consumption looking at implementation of Smart Grid in the society”. It can be found in the “Project overview” on the links of webpage.
Since the smart grid is a brand new technology, it is very unique case in Japan to measure its economical effect in the real society. Under these circumstances, urgently we found it very important to prove the evidence by using the world standard experimental framework and analysis that are already used in America, and to supply the efficient analysis result with the engineers and technical experts. Because there are not similar researches from economic perspective domestically, this research at laboratory of Ida, “The measurement of the effect of smart grid and the economical research project – Smart Grid Ecomy -” is a very pioneering research.
Experiments in the city
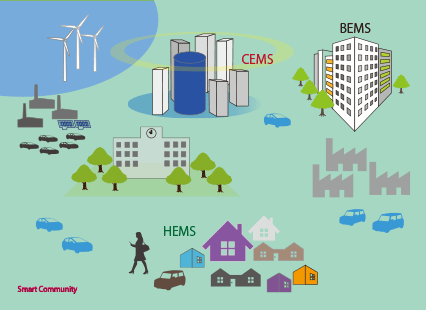
In 2010, Japanese began the concrete movement toward social proof of smart grid. The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry announced “Master plan to the energy for the next generation and social system proof” to research smart grid, and experiment began in these for regions: Yokohama-city of Kanagawa, Toyota-city of Aichi, Keihanna Gakkentoshi of Kyoto, and Kitakyushuu-city of Fukuoka.
(To learn more about this, please see the link below.)
In this 5 years of plan, we are targeting to find the way how smart grid and Smart City would work in Japan. This experiment is not only a research but carry the responsibility of the aspect of finding a new service or providing data outside Japan.
The Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry “Master plan to the energy for the next generation and social system proof”
The introduction of the experiment in each region. “The energy of the next generation and proof of the regional social system”
- Yokohama-city. (Yokohama-city project. (YSCP Project))
- http://jscp.nepc.or.jp/yokohama/index.shtml
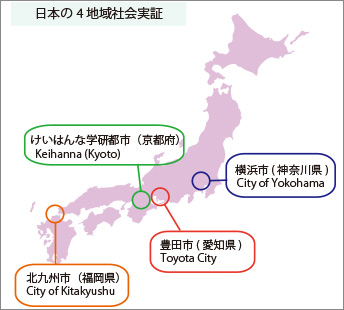
- Toyota-city: Toyota-city lower carbon social system proof project
(Smart Melit) – “Looking for the city where the cars and people prosper together” - http://jscp.nepc.or.jp/toyota/index.shtml
- Kyoto (Keihanna Gakkentoshi) “Keihanna Ecocity. The energy for the next generation / social system proof project”
- http://jscp.nepc.or.jp/keihanna/index.shtml
- Kitakyusyu-city: “Kitakyusyu-city smart community creative project”
- http://jscp.nepc.or.jp/kitakyushu/index.shtml
- At the laboratory of Ida, we have been advancing the proof experiment with the cooperation with these four regions and companies.
- ・Yokohama-city of Kanagawa (Toshiba, Tokyo Electric): Research of the effect of demand response to prosumer behavior of household with 4,000 solar system attached at maximum.
- Toyota-city of Aichi. (Toyota Corp, Cyubu Electric Power)
- ・Pursuing the saving energy style by introducing a plug-in and hybrid cars to newly-built smart houses.
- Kyoto Keihanna Gakkentoshi (Mitsubishi Heavy Industrial Corp, Kansai Electric Power)
- ・Leading a saving energy behavior by introducing the consultant and dynamic pricing to general households.
- Kitakyushu-city of Fukuoka(Nippon Steel & Sumitomo Metal, Fuji Electric)
- ・Measurement over the demand response effect by introducing the fluctuating dynamic pricing to condominium.
We, as an example, would like to talk about the detail of how the general household is doing in Kitakyusyu.
In 2012 summer and winter time, at Yahatahigashiku Higashida region of Kitakyushyu-city, we had a social proof of dynamic pricing for the first time ever in Japan. In this research, demands chosen randomly are separated into two groups: those who see the price change (group of treatment), and those who do not see it. We have done DR on treatment group setting 5 level of the pricing. (the price gets higher by each level.)
As a result,
・In the experiment of the summer time, we found that demand of treatment group was lowered at the peak of the price of electric being the highest. The higher the price, the lower the demand.
・In the experiment of the winter time, we found that demand of treatment group was lowered in both morning and evening time when the price gets the highest.
We also noticed a peak being shifted to the time zone of the finish of DR.
We confirmed that DR proof is effective according to this experiment.
For more info, please see below URL.
http://www.econ.kyoto-u.ac.jp/~ida/4Hoka/smagri/20121129kitakyushukisyarec.pdf
This result is almost as same as the one in America. And this experiment can be considered as a very important proof internationally in that it is the genuine dynamic pricing of RCT sort of experiment for the first time domestically and it proves the 5 level of fluctuating critical peak pricing that has never done in America.
And we only gather people who already joined the fluctuating pricing by the time for all electric household this time, meaning that if we try this on general household, we may expect bigger effect of the peak cut.
The more concern and the future expected
As we described, in the middle of the process of the possibility of the society and the city becoming smarter and smarter, various fields are attending the investigation and research including those mentioned above.
At the laboratory of Ida, considering the demand response perspective that we gained, we would like to continually search for the prevailing of DR from social proof to implement in the society. In order to do that, it is indispensible to have such a realistic policy that demands can become satisfied mentally and economically to live the daily lives.
And for the future, not only we step into a policy for a high added value of generating a power and protecting the environment, but also exporting the whole system of smart grid to those rising nations in which there is a dilemma between economical growth and protecting the environment, we would like to research for the field “for the future.”
Introdcution of Refereed documents of Smart Grid
- Takanori Ida (Website)
- Minister of Economy, Trade and Industry
- Announcement of master plans for the Demonstration of Next-Generation Energy and Social Systems
- METI, News Release
- Japan Smart City Portal(JSCP)
- Column (Tanaka, M. and T. Ida)
- HITACHI (Website)
- Kato,T(2011) Smart Power How to make a power-saving society save Japan! :Kadokawa Shoten
- Public Demonstration of Dynamic Pricing in the Kitakyushu Smart Community Creation Project
- Terms
- HEMS
- BEMS
- FEMS
- CEMS
- Smart meter
- Peak-cut
- Peak-shift
- Demand Response
- Dynamic Pricing
- TOU
- CPP
- RTP
- PTR
ADR
A balloon can be closed if it clicks the button which the upper right closes.
CEMS
A balloon can be closed if it clicks the button which the upper right closes.
CPP
A balloon can be closed if it clicks the button which the upper right closes.
DR
A balloon can be closed if it clicks the button which the upper right closes.
【HEMS】
(Home Energy Management System)
The system which supports the energy management in a home. The energy consumption apparatus in residences, such as an air-conditioner and lighting, is connected in a network, the surveillance of execution status or an energy consumption situation, history operation, an automatic occupation, etc. are performed, and energy saving and power saving are performed (it is a dummy text).
REP
A balloon can be closed if it clicks the button which the upper right closes.
RTP
A balloon can be closed if it clicks the button which the upper right closes.
TOU
A balloon can be closed if it clicks the button which the upper right closes.
【Smart meter】
Electric power meter equipped with the communication function.
What can connect between an electric power company and consumers, can exchange the data of the amount of the electric power used, etc., or can connect with the home electronics of the demand point, etc. and can control it (it is a dummy text)
Peak cut
A balloon can be closed if it clicks the button which the upper right closes.
【Peak shift】
In order to stop the peak of power consumption low, electricity usage is moved in time. For example, shift time to use electricity for the time zone of night with comparatively little electricity demand. (It is a dummy text)
Peak cut
A balloon can be closed if it clicks the button which the upper right closes.
【Peak shift】
In order to stop the peak of power consumption low, electricity usage is moved in time. For example, shift time to use electricity for the time zone of night with comparatively little electricity demand. (It is a dummy text)